K-Nearest Neighbors
The K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithm is a lazy learning model, meaning it does not build an explicit training model but rather stores the entire dataset for prediction. For each data point in the test set, KNN computes the distance, commonly using Manhattan, Euclidean, or Minkowski metrics, between the query point and all points in the training set. It then selects the \(k\) nearest neighbors (typically \(k = 5\)) based on these distances. Finally, the model predicts the outcome by applying majority voting for classification tasks or averaging the neighbors' values for regression tasks.
Implementation
The machine learning KNN model in Python was developed from scratch following the guidelines provided in [2]. The complete implementation script is available on KNN from Scratch.
Classifier
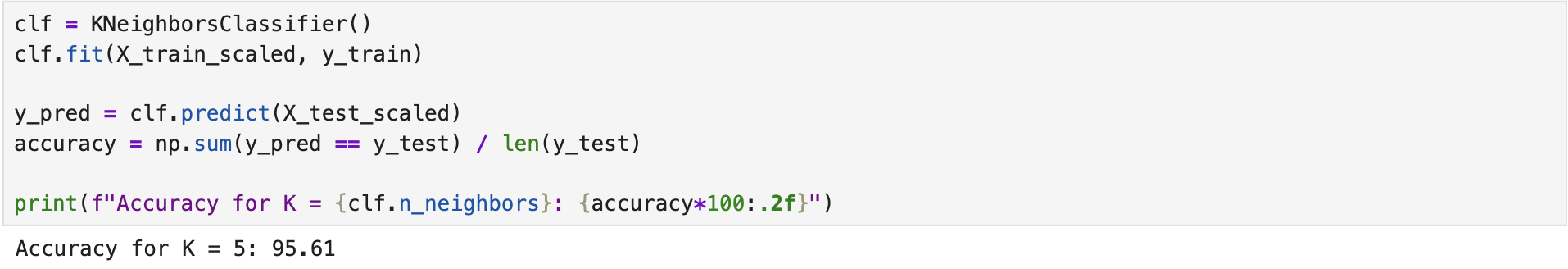
We developed a KNN classifier for the Breast Cancer dataset using the built-in functions provided in scikit-learn [1] in Python. The following screenshot illustrates the training process and the evaluation results of the model. The model was imported from sklearn.neighbors. The complete implementation script is available on the GitHub page KNN Classifier.
Regressor
We developed a KNN regressor using the California Housing dataset available in scikit-learn. The following screenshot shows the training (fitting) process the regressor, following by the evaluation results. The complete implementation script is available on the GitHub page KNN Regressor.

References
[1] F. Pedregosa, G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, V. Michel, B. Thirion, O. Grisel, M. Blondel, P. Prettenhofer, R. Weiss, V. Dubourg, J. Vanderplas, A. Passos, D. Cournapeau, M. Brucher, M. Perrot, and E. Duchesnay, “Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python,” Journal of Machine Learning Research, vol. 12, pp. 2825–2830, 2011.
[2] Misra Turp, “How to implement knn from scratch with python,” AssemblyAI, accessed: September 11, 2022, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rTEtEy5o3X0.

 IEEE
IEEE Web of Science
Web of Science