Sequential Graph
In addition to the input dimension, the number of nodes employed in a graph plays
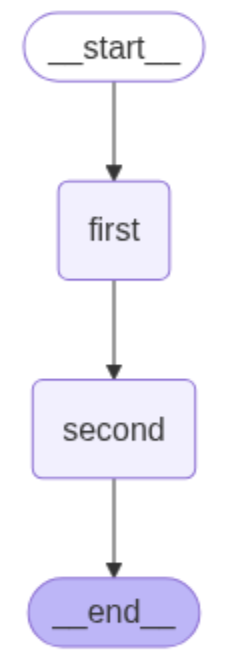
an important role in the efficiency of agentic systems. Figure 1 illustrates the
overall flow of a sequential graph in LangGraph, consisting of a start state, two
nodes (named first and second), and an end state. The start state is connected to
the first node via a directed edge (transition), and similarly, the second node is
connected to the first node and to the end state through two separate directed
edges [1].
In this example, the primary objective is to handle multiple nodes in a graph.
The nodes are responsible for sequentially process and update different parts
of the state. The first node receive the user's first name as input and add it
to the state. The second node receives the user's age and update the state.
Finally, the system outputs: "Hi {user’s first name}! You are {user’s age}
years old!". In this regard, we first need to create a shared data structure
to keep track of information as the application runs. The defined structure,

Then, the first node is defined as a function that receives the user's first name as input and incorporates it into the state information stored in AgentState. The function then returns the updated state [1].

Thereafter, the second node is defined as a function that receives the user's age as input and incorporates it into the state information stored in AgentState. The function then returns the updated state [1].

The next step involves constructing the graph. To begin, we initialize an empty graph in LangGraph, specifying its input type as state (AgentState). We then add the first and second nodes to the graph, followed by a proper connection. The first node is connected to the start state and the second node. The second node is connected to the end state. Finally, we compile the graph and store it in a variable for subsequent execution [1].

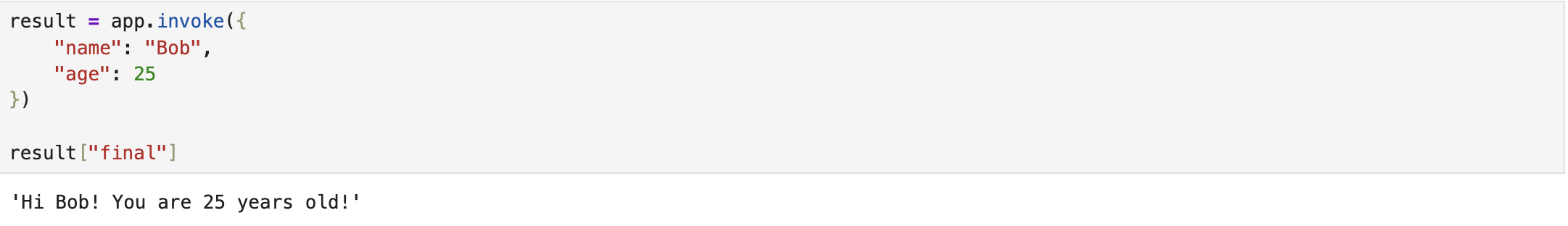
Lastly, we invoke the compiled graph by passing an example first name and age to that. The results indicate that the designed graph-based system could successfully meet the intended objective [1]. The complete implementation script is available on Sequential Graph.
References
[1] freeCodeCamp.org, https://youtu.be/jGg_1h0qzaM?si=69DsFmR2TMN259HC.

 IEEE
IEEE Web of Science
Web of Science